先来看nginx的配置文件格式,分层设计,通过大括号可以进行嵌套,层次最多4层。例如从http指令到index指令,共有4层。每个指令可以支持字符串/整数等类型参数,参数个数可以定制。
worker_processes 1;
error_log logs/error.log info;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
nginx的设计是高度模块化的,所以上面的每个配置指令都是在由各个模块各自定义的。例如worker_processes是由core模块定义,error_log是由errorlog模块定义,event由event模块定义,http由http模块定义。所以,配置文件的代码实际分为两部分,一部分为conf模块代码,负责配置文件读取解析,并且调用相应模块的函数处理所读取到的内容;另一部分为散落到各个模块的配置指令定义,以及处理函数。
配置文件读取这个功能完全围绕几个基本的数据结构进行设计,搞清楚数据结构,功能逻辑就很简单了。可以看出,nginx的设计和linus对于git的设计有异曲同工之妙,都是基于核心数据结构做精心设计之后,再完善功能。手中无剑,心中有剑,大致是这种境界。
-
配置文件使用
先了解在各个模块中配置文件是如何使用的。以event模块为例,ngx_core_conf_t是core模块的配置定义,ngx_event_conf_t是event模块的配置定义,在event模块中定义宏ngx_event_get_conf用于获取ngx_event_core_module模块的配置定义。
static ngx_int_t
ngx_event_process_init(ngx_cycle_t *cycle)
{
....
ngx_core_conf_t *ccf; //core模块的配置定义结构
ngx_event_conf_t *ecf; //event模块的配置定义结构
....
ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);
ecf = ngx_event_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_event_core_module);
所以,可以看出所有的配置信息都来自于cycle->conf_ctx这个上下文指针。看cycle结构体的定义,conf_ctx有四重指针,这个是和前面讲的配置文件四重嵌套对应的。
struct ngx_cycle_s {
void ****conf_ctx;
......
再看ngx_get_conf和ngx_event_get_conf的定义。ngx_events_module是一级模块,ngx_event_core_module是二级模块,ngx_event_get_conf先从conf_ctx中获取一级模块的ctx指针,再从一级ctx指针中获取二级模块的ctx index指向的内容。在模块逻辑中直接使用最后转换的结构体ecf就可以了。
#define ngx_get_conf(conf_ctx, module) conf_ctx[module.index]
#define ngx_event_get_conf(conf_ctx, module) \
(*(ngx_get_conf(conf_ctx, ngx_events_module))) [module.ctx_index];
event模块比较简单,很适合理解配置文件机制。http模块就要复杂很多,看起来比较繁杂。
-
配置文件解析
那么配置文件是如何解析为conf_ctx的内容,就需要借助ngx_conf_t。
struct ngx_conf_s {
char *name; //当前解析到的指令
ngx_array_t *args; //指令参数
ngx_cycle_t *cycle;
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_pool_t *temp_pool;
ngx_conf_file_t *conf_file;
ngx_log_t *log;
void *ctx;
ngx_uint_t module_type; //模块类型
ngx_uint_t cmd_type; //指令类型
ngx_conf_handler_pt handler; //自定义解析函数
char *handler_conf; //传给handler处理的模块conf
};
其中ctx变量和cycle->conf_ctx是相等的。在ngx_init_cycle中,初始化conf结构之后,就根据conf结构调用ngx_conf_parse来解析配置文件。
ngx_init_cycle(ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle)
{
ngx_conf_t conf;
......
conf.ctx = cycle->conf_ctx;
conf.cycle = cycle;
conf.pool = pool;
conf.log = log;
conf.module_type = NGX_CORE_MODULE; //在ngx_conf_handler将会用到
conf.cmd_type = NGX_MAIN_CONF;
......
if (ngx_conf_param(&conf) != NGX_CONF_OK) {
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}
if (ngx_conf_parse(&conf, &cycle->conf_file) != NGX_CONF_OK) {
//这里传入了conf_file,初始化配置文件fd
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}
......
ngx_conf_parse是配置文件解析的核心函数,主要工作就是解析文件,将结果放到对应模块的结构体。这个函数会被多次调用,如果一级模块的配置项需要嵌套,则在一级模块的指令set函数中就需要调用ngx_conf_parse。所以,在第一次调用时,初始化模块类型为core和conf的指令,即event/http/log/mail/regex这几个一级模块的指令。这些一级模块如果有嵌套指令,则在各自的block解析函数中调用ngx_conf_parse,例如:ngx_events_block和ngx_http_block,block函数完成二级及其嵌套指令解析。
ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename)
{
......
for ( ;; ) {
rc = ngx_conf_read_token(cf);
......
/* rc == NGX_OK || rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START */
//解析一个完整指令之后,进入handler处理
rc = ngx_conf_handler(cf, rc);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
goto failed;
}
}
......
先看模块指令的结构体定义,其中type定义了指令的层级和参数个数,例如NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK定义了一个可嵌套二级指令的一级指令,NGX_EVENT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1定义了一个event模块只有一个参数的二级指令。
struct ngx_command_s {
ngx_str_t name; //指令名
ngx_uint_t type; //指令类型
char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf); //指令处理函数,根据类型,有int,str,flag等预置函数可用
ngx_uint_t conf;
ngx_uint_t offset; //变量在模块conf结构体中的偏移
void *post; //后处理函数
};
ngx_conf_handler遍历当前所有模块,查找与当前指令匹配的command定义,并调用set函数,完成配置项读取赋值。
ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last)
{
......
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
/* look up the directive in the appropriate modules */
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CONF_MODULE
&& ngx_modules[i]->type != cf->module_type)
{
//判断模块类型,只处理cf->module_type指示的模块,或者conf
continue;
}
cmd = ngx_modules[i]->commands;
if (cmd == NULL) {
continue;
}
for ( /* void */ ; cmd->name.len; cmd++) {
//遍历模块的所有指令,找到匹配的cmd
if (name->len != cmd->name.len) {
continue;
}
if (ngx_strcmp(name->data, cmd->name.data) != 0) {
continue;
}
......
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) {
conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[ngx_modules[i]->index];
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_MAIN_CONF) {
//由于指令需要嵌套,所以conf赋值为二级指针
conf = &(((void **) cf->ctx)[ngx_modules[i]->index]);
} else if (cf->ctx) {
confp = *(void **) ((char *) cf->ctx + cmd->conf);
if (confp) {
conf = confp[ngx_modules[i]->ctx_index];
}
}
//调用set函数,即具体模块中的指令读取函数
//对于http模块的解析函数ngx_http_block,这里传入的conf指针为空,
//所以具体的内存分配,完全由模块的解析函数决定,自由度很高。
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
......
-
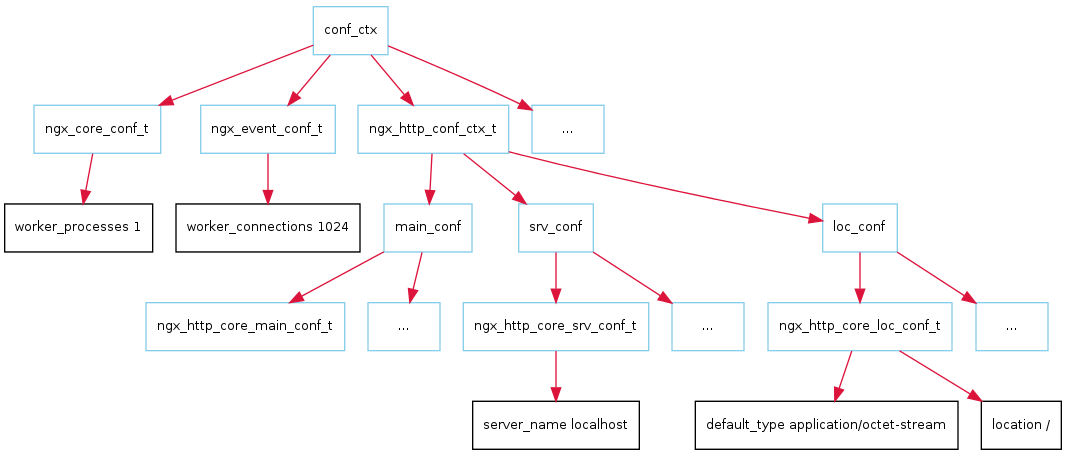
总结
最后用一个图来描述一下配置文件在内存中的存储。